Effectiveness of the Sugar and Stevia Consumption Program on the Control Blood Glucose Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Patients at Pak Thong Chai District Nakhon Ratchasima Province
Main Article Content
Abstract
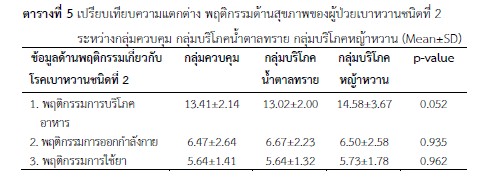
Diabetes is a disorder of blood sugar control. If patients have poor control over their diet of starches and sugars, it will lead to complications. However, controlling sugar consumption is difficult. The researchers therefore designed a program to help control blood sugar levels more efficiently and conveniently for patients. The purpose of this research was to study the effectiveness of the sugar and stevia consumption program on controlling blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes using a randomized control trial (RCT). The sample groups consisted of 102 out-patients at Pak Thong Chai Hospital with type 2 diabetes, divided into 3 groups of 34 people each: namely a control group consuming normal food; a group given 24 grams of sugar per day (the sugar consumption group); and a stevia consumption group for a period of 90 days. Following the program, the volunteers who consumed granulated sugar and those who consumed stevia showed FBS blood sugar values of 129.35 and 130.38, respectively, and cumulative blood sugar levels (HbA1c) of 6.27 and 6.12, respectively. In addition, both FBS blood sugar and cumulative average blood sugar (HbA1c) decreased without affecting the change in body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes, and the values were significantly lower than those in the control group (p<0.05). As a result, a program with a daily sugar intake of 24 grams and consuming stevia extract instead of table sugar was able to control blood sugar levels better than a program for volunteers who received only normal dietary advice.
Article Details
References
เจนพล แก้วกิติกุล. (2566, 10 มิถุนายน). ระดับน้ำตาลสะสมในเลือดของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 คลินิกหมอครอบครัวป่างิ้ว อำเภอเวียงป่าเป้า จังหวัดเชียงราย. [เอกสารนำเสนอ] ใน การประชุมวิชาการ “คลังปัญญาเชียงราย” สำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดเชียงราย ครั้งที่ 8, เชียงราย, ประเทศไทย.
ยุทธนา สังขวรรณ. (2555). ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์ดัชนีมวลกายของผู้นำหมู่บ้านที่เข้าร่วมโครงการ คนแม่อายไร้พุง เทิดไท้องค์ราชัน อำเภอแม่อาย จังหวัดเชียงใหม่. [วิทยานิพนธ์มหาบัณฑิต]. มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา
วรรณี นิธิยานันท์. (2562, 24 มีนาคม). ไทยป่วยเบาหวานพุ่งสูงต่อเนื่อง. https://www.thaihealth.or.th/Content/50527
สุปราณี เฟื่องฟู, จุฬารักษ์ กวีวิวิธชัย และนพวรรณ เปียซื่อ. (2558). ผลโปรแกรมควบคุมอาหารโดยใช้หลักอาหารแลกเปลี่ยนต่อความรู้ พฤติกรรมสุขภาพ และระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยที่เป็นเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบล. วารสารพยาบาลสาธารณสุข, 29(3), 34-49.
สุวรรณชัย วัฒนายิ่งเจริญชัย. (2566, 5 กรกฎาคม). กรมอนามัยชี้ ความหวาน มีประโยชน์หรือโทษขึ้นอยู่กับปริมาณ. https://multimedia.anamai.moph.go.th/news/050766/
สำนักงานโภชนาการ กรมอนามัย. (2562, 25 พฤษภาคม). สุขภาพที่ดี เริ่มที่อาหาร ลดหวาน มัน เค็ม เติมเต็ม ผัก ผลไม้. https://planning.anamai.moph.go.th/อาหารลดหวาน
อนัญญา คูอาริยะกุล. (2564). การพัฒนารูปแบบการดูแลสุขภาพตนเองของผู้ป่วยความดันโลหิตสูงในการป้องกันการเกิดโรคไตเรื้อรังโดยการมีส่วนร่วมของชุมชนตำบลป่าเซ่า อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดอุตรดิตถ์. วารสารวิจัยสุขภาพและการพยาบาล, 37(3), 51-63.
Dandan, W., Hong, H. & Cong W. (2023). Cellular and potential molecular mechanisms underlying transovarial transmission of the obligate symbiont Sulcia in cicadas. Environmental Microbiology, 25(4), 836-852. http://DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.16310
Ji-Soo, Y., Suk-Jeong, L., Hyun-Chul, L., & Mi-Ja, K. (2007). The Effect of a Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification Program on Glycemic Control and Body Composition in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Asian Nursing Research, 1(2), 106-115.
Silvio, E. I., Richard, M. B., John, B. B., Michaela, D., Ele, F., Michael, N., Anne, L. P., Apostolos, T., Richard, W., & David, R. M. (2015). Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2015: A Patient-Centered Approach: Update to a Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 38(1), 140-149.
Uranee, R., Kerada, K., Apiradee S., & Chutatip, V. (2013) The Effects of a Diabetic Self-management Program on Knowledge, Behavior, and Health Indexes among People with Type 2 Diabetes. Journal of Nursing Science, 31(1), 7-18.