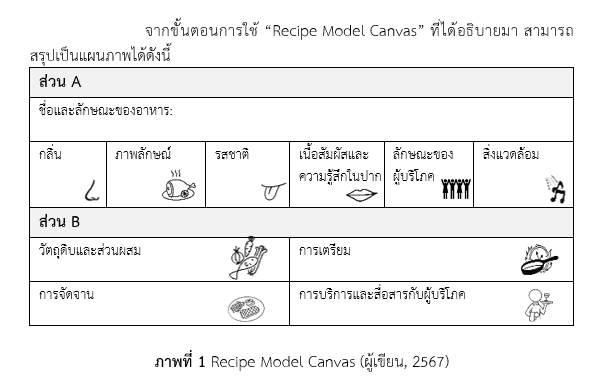
Recipe Model Canvas: A Structured Tool for Creative Recipe Development
Main Article Content
Abstract
This article introduces the concept of the Recipe Model Canvas (RMC), a tool designed to systematically support the creation and development of recipes in the highly competitive food and beverage industry in Thailand. The RMC integrates key factors influencing consumer choices and satisfaction, including sensory aspects, environmental contexts, and individual consumer characteristics. By incorporating these factors, the RMC facilitates effective planning, quality control, and product development, enabling businesses to meet consumer demands comprehensively and efficiently.
Moreover, the RMC is particularly suitable for creating innovative menus that add value to food businesses, especially in contexts requiring unique dining experiences, such as utilizing Molecular Gastronomy techniques. To enhance the potential of the RMC, further studies should explore the relationships among the factors affecting consumers and adapt the tool to fit diverse cultural contexts and international markets. This development will empower businesses to increase their competitive advantage and promote sustainable growth in the long term.
Article Details
References
ศุภกร กรบุญไตรทศ. (2567, มิถุนายน 11). แนวโน้มธุรกิจ/อุตสาหกรรม ปี 2567-2569: ธุรกิจร้านอาหารและเครื่องดื่ม. https://www.krungsri.com/th/research/industry/industry-outlook/services/food-beverages/io/io-food-beverage-restaurant-2024-2026.
Andersen, B. V., & Hyldig, G. (2015). Consumers’ view on determinants to food satisfaction. A qualitative approach. Appetite, 95(12), 9-16.
Ashari, M. F. S., Siregar, Z. M. E., & Halim, A. (2023). The influence of service quality, taste, and perceived price on customer loyalty by mediating customer satisfaction. Quantitative Economics and Management Studies, 4(3), 474-485.
Bärebring, L., Palmqvist, M., Winkvist, A., & Augustin, H. (2020). Gender differences in perceived food healthiness and food avoidance in a Swedish population-based survey: A cross-sectional study. Nutrition Journal, 19(1), 1-8.
Beauchamp, G. K. (2016). Why do we like sweet taste: a bitter tale?. Physiology & Behavior, 164(10), 432-437.
Daly, A. N., O'Sullivan, E. J., & Kearney, J. M. (2022). Considerations for health and food choice in adolescents. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 81(1), 75-86.
Davis, L. A., & Running, C. A. (2023). Good is sweet and bad is bitter: Conflation of affective value of aromas with taste qualities in untrained participants. Journal of Sensory Studies, 38(3), e12820.
Fukutani, Y., Abe, M., Saito, H., Eguchi, R., Tazawa, T., de March, C. A., Nishida, T., Kumagai, M., Mori, K., & Matsunami, H. (2023). Antagonistic interactions between odorants alter human odor perception. Current Biology, 33(11), 2235-2245.
García-Segovia, P., García Alcaraz, V., Tárrega, A., & Martínez-Monzó, J. (2020). Consumer perception and acceptability of microalgae based breadstick. Food Science and Technology International, 26(6), 493-502.
Gil, M., Rudy, M., Stanistawczyk, R., Duma-Kocan, P., & Zurek, J. (2022). Gender differences in eating habits of Polish young adults aged 20–26. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15280.
Gisslen, W. (2018). Professional Cooking (9th ed.). Wiley.
Greis, M., Nolden, A. A., Kinchla, A. J., Puputti, S., Seppä, L., & Sandell, M. (2023). What if plant-based yogurts were like dairy yogurts? Texture perception and liking of plant-based yogurts among US and Finnish consumers. Food Quality and Preference, 107(4), 104848.
Ilban, M. O., & Yıldız, N. (2020). The role of local cuisine satisfaction and consumer trust in creating customer loyalty towards destinations: The case of Sakarya/Adapazarı (Turkish cuisine). Güncel Turizm Araştırmaları Dergisi, 4(2), 240-260.
Imtiyaz, H., Soni, P., & Yukongdi, V. (2021). Role of sensory appeal, nutritional quality, safety, and health determinants on convenience food choice in an academic environment. Foods, 10(2), 345.
Indajang, K., Candra, V., Sianipar, M. Y., Sembiring, L. D., & Simatupang, S. (2023). The effect of service quality and price on customer satisfaction. Ekonomi, Keuangan, Investasi Dan Syariah (Ekuitas), 4(3), 942-950.
Labensky, S. R., Hause, A. M., & Martel, P. A. (2024). On Cooking: A Textbook of Culinary Fundamentals (7th ed.). Pearson.
Leonor, F. D. C. (2014). Effect of nostalgia triggered by sound: from the sound of the sea dish: on flavour perception [Master’s Degree]. Estoril Higher Institute for Tourism and Hotel Studies.
Mac Con Iomaire, M., Afifi, M. F., & Healy, J. J. (2021). Chefs’ perspectives of failures in foodservice kitchens, part 1: A phenomenological exploration of the concepts, types, and causes of food production failure. Journal of Foodservice Business Research, 24(2), 177-214.
Nakauma, M., & Funami, T. (2021). Structuring for elderly foods. Food Hydrocolloids, Springer.
Qurnia, M. D., & Prabawati, A. (2021). The Effect of Food Quality and Physical Environment on Revisit Interests with Consumer Satisfaction as Mediation Variable. JMM17: Jurnal Ilmu Ekonomi dan Manajemen, 8(02), 81-90.
Reddy, G., & van Dam, R. M. (2020). Food culture and identity in multicultural societies: Insights from Singapore. Appetite, 149(6), 104633
Romagny, S., Ginon, E., & Salles, C. (2017). Impact of reducing fat, salt and sugar in commercial foods on consumer acceptability and willingness to pay in real tasting conditions: A home experiment. Food Quality and Preference, 56(3), 164-172.
Sen, A. (2023). Plating for Perfection: An Exploration of Techniques for Optimal Food Decorating Strategies and Aesthetic Visual Appeal in Indian Cuisine. Asian Journal of Food Research and Nutrition, 2(4), 612-624.
Siangphloen, P., Shepherd, D., Kantono, K., & Hamid, N. (2024). Lunch melodies: Investigating the impact of music on emotions, hunger, liking, and psychophysiology while viewing a lunch meal. Food Research International, 192(9), 114825.
Snowden, R. J., Snowden, R., Thompson, P., & Troscianko, T. (2012). Basic vision: an introduction to visual perception, Oxford University Press.
The Culinary Institute of America. (2011). The professional chef (9th ed.). Wiley.
Wen, Q., Wei, Y., Du, H., Lv, J., Guo, Y., Bian, Z., ... & Li, L. (2021). Characteristics of spicy food consumption and its relation to lifestyle behaviours: Results from 0.5 million adults. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 72(4), 569-576.
Yamim, A. P., Mai, R., & Werle, C. O. (2020). Make it hot? How food temperature (mis)guides product judgments. Journal of Consumer Research, 47(4), 523-543.
Zhang, Y., Venkitasamy, C., Pan, Z., Liu, W., & Zhao, L. (2017). Novel umami ingredients: Umami peptides and their taste. Journal of Food Science, 82(1), 16-23.